- Computed tomography (CT) imaging provides a form of imaging known as cross-sectional imaging. CT imaging produces cross-sectional images of anatomy.
- The Nikon XT H 225 ST is a Computed Tomography (CT) system ideally suited to a wide range of materials and sample sizes, especially those that are too large or heavy for other systems in the range. The system has three interchangeable sources; the 225 kV reflection target, 180 kV transmission target and the optional.
- MIC offers Computed Tomography (CT) colonography, or virtual colonoscopy, to screen for early signs of colorectal cancer such as polyps or tumors.
- The technology of medical imaging has undergone a tremendous change since the Nobel prize-winning development of computed tomography. Becoming knowledgeable about advanced imaging technology is essential for the radiologic technologist to grow with the field.
MicroComputed tomography is an X-ray transmission image technique. X-rays are emitted from an X-ray generator, travel through a sample, and are recorded by a detector on the other side to produce radiograph (known as projection image- Figure 1).
Conventional X-ray Images
Figure 1: Chest X ray Image
Splashtop Wired XDisplay Free Android latest 1.0.0.11 APK Download and Install. Use your Android as an extra monitor to your PC! Splashtop Wired XDisplay. Discount as $6.99 for initial launch (regular price: $12.99)!. Use your Android as an extra monitor to your PC!. Developed by the Creator of Splashtop Remote Desktop, the best remote desktop app developer, with over 20 million users! Hero Mod Apk Roblox Mod APK StoryArt Mod APK 8 Ball Pool Mod. Splashtop Wired XDisplay turns an Android into an extra display for your computer, enhancing productivity. First you must uninstall Splashtop Wired XDisplay original version if you have installed it. Then, download Splashtop Wired XDisplay Mod APK on our site. After completing the download, you must find the apk file and install it. You must enable 'Unknown sources' to install applications outside the Play Store. Splashtop Wired XDisplay (Package Name: com.splashtop.xdisplay.wired.pro) is developed by Splashtop and the latest version of Splashtop Wired XDisplay 1.0.0.11 was updated on May 9, 2018. Splashtop Wired XDisplay is in the category of Tools. Descargar splashtop wired xdisplay pro apk.
All x-ray imaging is based on the absorption of x rays as they pass through the different parts of a patient's body. Depending on the amount absorbed in a particular tissue such as muscle or lung, a different amount of x rays will pass through and exit the body. The amount of x rays absorbed contributes to the radiation dose to the patient. During conventional x-ray imaging, the exiting x rays interact with a detection device (x-ray film or other image receptor) and provide a 2-dimensional projection image of the tissues within the patient's body - an x-ray produced 'photograph' called a 'radiograph.' The chest x ray (Figure 1) is the most common medical imaging examination. Pokemon rijon adventures download gba. During this examination, an image of the heart, lungs, and other anatomy is recorded on the film.
Computed Tomography (CT)
Figure 2: Cross-sectional Image of Abdomen

Although also based on the variable absorption of x rays by different tissues, computed tomography (CT) imaging, also known as 'CAT scanning' (Computerized Axial Tomography), provides a different form of imaging known as cross-sectional imaging. The origin of the word 'tomography' is from the Greek word 'tomos' meaning 'slice' or 'section' and 'graphe' meaning 'drawing.' A CT imaging system produces cross-sectional images or 'slices' of anatomy, like the slices in a loaf of bread. The cross-sectional images (Figure 2) are used for a variety of diagnostic and therapeutic purposes. Information regarding whole body CT screening can be found here: https://www.fda.gov/radiation-emitting-products/medical-x-ray-imaging/other-information-resources-related-whole-body-ct-screening
How a CT system works
Figure 3: Patient in CT Imaging System
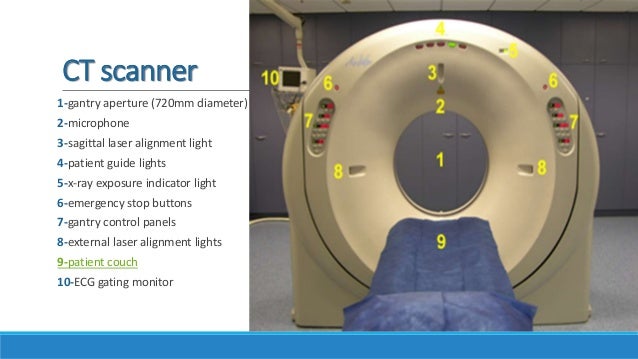
- A motorized table moves the patient (Figure 3) through a circular opening in the CT imaging system.
- As the patient passes through the CT imaging system, a source of x rays rotates around the inside of the circular opening. A single rotation takes about 1 second. The x-ray source produces a narrow, fan-shaped beam of x rays used to irradiate a section of the patient's body (Figure 4). The thickness of the fan beam may be as small as 1 millimeter or as large as 10 millimeters. In typical examinations there are several phases; each made up of 10 to 50 rotations of the x-ray tube around the patient in coordination with the table moving through the circular opening. The patient may receive an injection of a 'contrast material' to facilitate visualization of vascular structure.
- Detectors on the exit side of the patient record the x rays exiting the section of the patient's body being irradiated as an x-ray 'snapshot' at one position (angle) of the source of x rays. Many different 'snapshots' (angles) are collected during one complete rotation.
- The data are sent to a computer to reconstruct all of the individual 'snapshots' into a cross-sectional image (slice) of the internal organs and tissues for each complete rotation of the source of x rays.

Advances in Technology and Clinical Practice
Figure 4: CT Fan Beam
Today most CT systems are capable of 'spiral' (also called 'helical') scanning as well as scanning in the formerly more conventional 'axial' mode. In addition, many CT systems are capable of imaging multiple slices simultaneously. Such advances allow relatively larger volumes of anatomy to be imaged in relatively less time. Another advancement in the technology is electron beam CT, also known as EBCT. Although the principle of creating cross-sectional images is the same as for conventional CT, whether single- or multi-slice, the EBCT scanner does not require any moving parts to generate the individual 'snapshots.' As a result, the EBCT scanner allows a quicker image acquisition than conventional CT scanners.
Some Photos Copyright © 2002, GettyImages
Mic Computed Tomography Program
Required Reports for Industry
